
Research
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a systemic autoimmune disease that particularly affects women in the childbearing years and is characterized by diverse clinical features. In addition to the fatigue, cognitive impairment and skin disease that impact many patients, severe organ involvement can include damage to kidneys, cardiovascular system and central nervous system. Generation of autoantibodies targeting DNA, RNA or DNA- or RNA-binding proteins and sustained production of type I interferon are core features of the immunopathogenesis of SLE, contributing to tissue inflammation and damage. We are particularly interested in unraveling the mechanisms that initiate autoimmunity and target the immune response to intracellular particles containing nucleic acids and associated proteins, such as the nucleosome and the spliceosome. We have demonstrated activation of the type I interferon pathway in patients with SLE and its association with autoantibodies targeting RNA binding proteins, pointing to the role of Toll-like receptor 7 as a sensor of RNA that induces interferon production. Our lab's research is based on detailed study of an informative longitudinal patient cohort, with clinical data and blood samples collected over time, allowing for dissection of the underlying biologic mechanisms that contribute to specific disease manifestations and disease flares. Current studies are characterizing subsets of patients based on genetic variants, autoantibody profiles and clinical features of disease, with interest in the determinants of lupus nephritis and chronic tissue damage. Identification of rational therapeutic targets is a goal of the lab, with our previous research having supported CD40 ligand and the type I interferon pathway as targets.
Figure: Significant mechanisms contributing to pathogenesis of SLE.
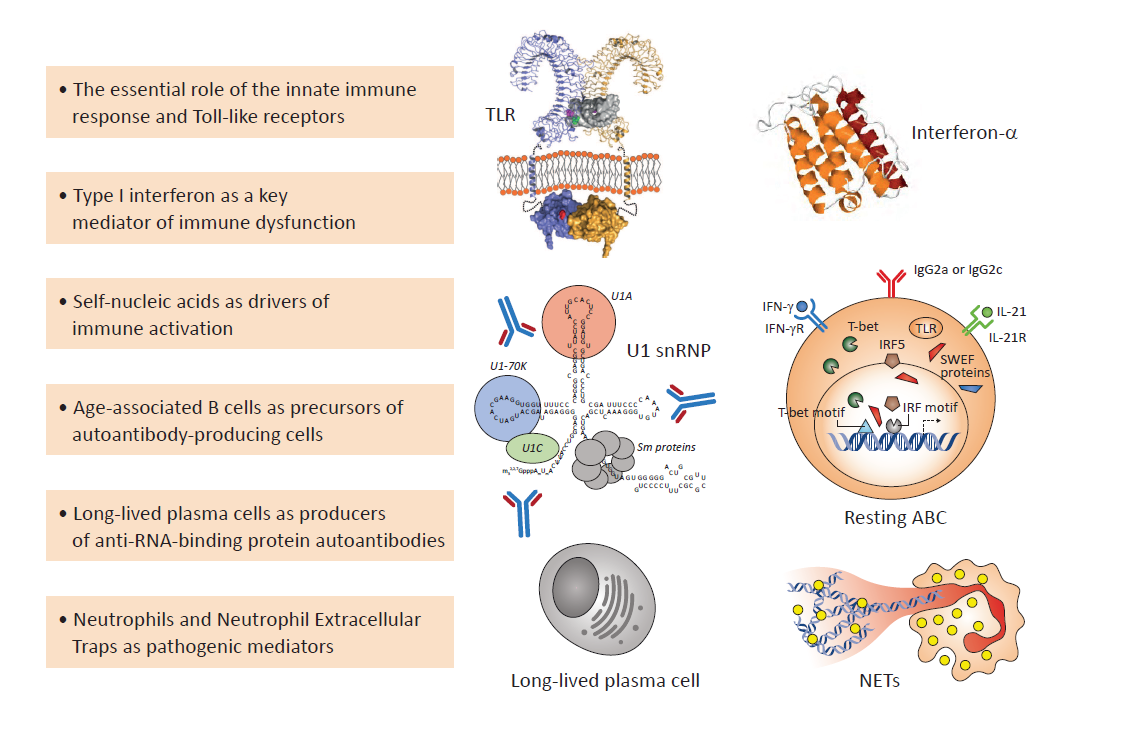
Current Projects:
- Pathogenic mechanisms distinguishing SLE patients based on autoantibody profiles
- Molecular pathways mediating active lupus nephritis
- Clinical consequences of lupus-associated coding gene variants
Bio
Dr. Crow received her medical degree from Cornell Medical College, internal medicine training at New York Presbyterian Hospital and rheumatology fellowship training at Hospital for Special Surgery. She was a post-doctoral research fellow in the laboratory of Dr. Henry Kunkel at Rockefeller University prior to joining the rheumatology faculty at Hospital for Special Surgery and Weill Cornell Medical College. In addition to her research activities, Dr. Crow served as Physician-in-Chief of Hospital for Special Surgery from 2010-2020 and as the Chair of the Scientific Advisory Board of the Lupus Research Alliance. She is currently chair of the Medical and Scientific Advisory Committee of the Arthritis Foundation and serves on the foundation's Board of Trustees.
Distinctions:
- President, Henry Kunkel Society (2007-2009)
- Margaret D. Smith Lifetime Achievement Award, Arthritis Foundation (2010)
- Master, American College of Rheumatology (2012)
- Presidential Gold Medal, American College of Rheumatology (2018)
- Lee C. Howley, Sr. Prize in Arthritis Scientific Research (2022)
Selected Publications:
Crow MK. Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus: risks, mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 Aug;82(8):999-1014. PMID: 36792346.
Crow MK. Advances in lupus therapeutics: Achieving sustained control of the type I interferon pathway. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2022 Dec;67:102291. PMID: 36183477.
Barrat FJ, Crow MK, Ivashkiv LB. Interferon target-gene expression and epigenomic signatures in health and disease. Nat Immunol. 2019 Dec;20(12):1574-1583. PMID: 31745335.
Crow MK, Olferiev M, Kirou KA. Type I Interferons in Autoimmune Disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2019 Jan 24;14:369-393. PMID: 30332560.
Mavragani CP, Sagalovskiy I, Guo Q, Nezos A, Kapsogeorgou EK, Lu P, Liang Zhou J, Kirou KA, Seshan SV, Moutsopoulos HM, Crow MK. Expression of Long Interspersed Nuclear Element 1 Retroelements and Induction of Type I Interferon in Patients With Systemic Autoimmune Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Nov;68(11):2686-2696. PMID: 27338297.
